Connection of the radius and ulna. Elbow bone
Ulna, long. V. it distinguishes between a body and two epiphyses—proximal and distal. The body of the ulna, corpus ulnae, is triangular in shape. It has three edges: anterior (palmar), posterior (dorsal) and interosseous (outer) - and three surfaces.
The structure of the ulna.
The anterior edge, margo anterior, is rounded; the posterior edge, margo posterior, is directed backward, and the interosseous edge, margo interosseus, is pointed and turned to the side radius.
Ulna video
Front surface facies anterior, somewhat concave. On it there is a nutrient opening, foramen nutricium, which leads into the proximally directed nutrient tubule, canalis nutricius. In the upper part of the anterior surface, on the border between the body and upper end bones, the tuberosity of the ulna is located, tuberositas ulnae. The posterior surface, facies posterior, faces backward, and the medial surface, facies medialis, faces the inner edge of the forearm.
Upper, or proximal, epiphysis, epiphysis proximalis, thickened, continues upward into the olecranon, olecranon. The anterior surface of this process is occupied by a trochlear notch, incisura trochlearis, which is limited below by the coronoid process, processus coronoideus. On the outer surface coronoid process there is the radial notch, incisura radialis, - the place of articulation of the ulna with the articular circumference of the head of the radius. Behind the radial notch, the ridge of the supinator begins. Christa M. supinatoris, which, following down, reaches upper sections bone body.
Lower, or distal, epiphysis, epiphysis distalis, the ulna is rounded. It shows the head of the ulna, caput ulnae. The surface of the head facing the wrist is smooth and concave. Along the periphery of the head is located articular surface, - articular circumference, circumferentia articularis, of the ulna, articulating with the radius. The medial-posterior surface of the head continues into the styloid process, processus styloideus; it can be easily felt through the skin. Elbow joint read
Ulna, ulna. The upper (proximal) thickened end of the ulna (epiphysis) is divided into two processes: the posterior, thicker, olecranon, olecranon, and the anterior, small, coronoid, processus coronoideus. Between these two processes there is a trochlear notch, incisura trochlearis, which serves for articulation with the trochlea of the humerus.
On the radial side of the coronoid process there is a small incisura radialis - the place of articulation with the head of the radius, and in front under the coronoid process there is a tuberosity, tuberositas ulnae, the place of attachment of the tendon m. brachialis. The lower (distal) end of the ulna bears a round head with a flat lower surface, caput ulnae (epiphysis), from which medial side the styloid process, processus styloideus (apophysis), arises. The head has an articular surface around its circumference, circumferentia articularis, a place of articulation with the adjacent radius.
Which doctors should I contact to examine the ulna:
Traumatologist
What diseases are associated with the ulna:
What tests and diagnostics need to be done for the ulna:
X-ray of the forearm
Is something bothering you? Do you want to know more detailed information about the ulna or do you need an examination? You can make an appointment with a doctor– clinic Eurolab always at your service! The best doctors will examine you, advise you, provide necessary help and make a diagnosis. you also can call a doctor at home. Clinic Eurolab open for you around the clock.
How to contact the clinic:
Phone number of our clinic in Kyiv: (+38 044) 206-20-00 (multi-channel). The clinic secretary will select a convenient day and time for you to visit the doctor. Our coordinates and directions are indicated. Look in more detail about all the clinic’s services on it.
If you have previously performed any research, Be sure to take their results to a doctor for consultation. If the studies have not been performed, we will do everything necessary in our clinic or with our colleagues in other clinics.
It is necessary to take a very careful approach to your overall health. There are many diseases that at first do not manifest themselves in our body, but in the end it turns out that, unfortunately, it is too late to treat them. To do this, you just need to do it several times a year. be examined by a doctor to not only prevent terrible disease, but also to maintain a healthy spirit in the body and the organism as a whole.
If you want to ask a doctor a question, use the online consultation section, perhaps you will find answers to your questions there and read self care tips. If you are interested in reviews about clinics and doctors, try to find the information you need on. Also register on medical portal Eurolab to stay up to date latest news and updates on information about the Ulna on the site, which will be automatically sent to you by email.
Other anatomical terms starting with the letter "L":
| Forehead |
| Face |
| Elbow |
| Lungs |
| Lymph |
| The lymph nodes |
| Leukocytes |
| Elbow joint |
| Wrist joint |
| Spatula |
| Radius |
| pubic bone |
| Ankle |
| Lymphocytes |
| Bulb of the vestibule of the vagina |
| Left atrium |
| Left ventricle |
| Pulmonary trunk |
| Pulmonary veins |
| Radial artery |
| Ulnar artery |
| Lymphatic vessels |
Ulna, ulna. The upper (proximal) thickened end of the ulna (epiphysis) is divided into two processes: the posterior, thicker, olecranon, olecranon, and the anterior, small, coronoid, processus coronoideus. Between these two processes there is a trochlear notch, incisura trochlearis, which serves for articulation with the trochlea of the humerus.
On the radial side of the coronoid process there is a small incisura radialis - the place of articulation with the head of the radius, and in front under the coronoid process there is a tuberosity, tuberositas ulnae, the place of attachment of the tendon m. brachialis. The lower (distal) end of the ulna bears a round head with a flat lower surface, caput ulnae (epiphysis), from which the styloid process, processus styloideus (apophysis), extends from the medial side. The head has an articular surface around its circumference, circumferentia articularis, a place of articulation with the adjacent radius.
Which doctors should I contact to examine the ulna:
Traumatologist
What diseases are associated with the ulna:
What tests and diagnostics need to be done for the ulna:
X-ray of the forearm
Is something bothering you? Do you want to know more detailed information about the Ulna or do you need an examination? You can make an appointment with a doctor– clinic Eurolab always at your service! The best doctors will examine you, advise you, provide the necessary assistance and make a diagnosis. you also can call a doctor at home. Clinic Eurolab open for you around the clock.
How to contact the clinic:
Phone number of our clinic in Kyiv: (+38 044) 206-20-00 (multi-channel). The clinic secretary will select a convenient day and time for you to visit the doctor. Our coordinates and directions are indicated. Look in more detail about all the clinic’s services on it.
If you have previously performed any research, Be sure to take their results to a doctor for consultation. If the studies have not been performed, we will do everything necessary in our clinic or with our colleagues in other clinics.
It is necessary to take a very careful approach to your overall health. There are many diseases that at first do not manifest themselves in our body, but in the end it turns out that, unfortunately, it is too late to treat them. To do this, you just need to do it several times a year. be examined by a doctor, in order not only to prevent a terrible disease, but also to maintain a healthy spirit in the body and the organism as a whole.
If you want to ask a doctor a question, use the online consultation section, perhaps you will find answers to your questions there and read self care tips. If you are interested in reviews about clinics and doctors, try to find the information you need on. Also register on the medical portal Eurolab, to be constantly aware of the latest news and updates about the Ulna on the site, which will be automatically sent to you by email.
Other anatomical terms starting with the letter "L":
| Forehead |
| Face |
| Elbow |
| Lungs |
| Lymph |
| The lymph nodes |
| Leukocytes |
| Elbow joint |
| Wrist joint |
| Spatula |
| Radius |
| pubic bone |
| Ankle |
| Lymphocytes |
| Bulb of the vestibule of the vagina |
| Left atrium |
| Left ventricle |
| Pulmonary trunk |
| Pulmonary veins |
| Radial artery |
| Ulnar artery |
| Lymphatic vessels |
The tubular bone, which has a triangular shape and is located in the hand, is called the ulna. It is often injured, so know the location, anatomy, possible injuries and methods of therapy are necessary.
The tubular bone is located in the area from the hand to the bend of the elbow. It has a trihedron shape and has 3 surfaces:
- front;
- back;
- medial.
In addition, the ulna has three edges: lateral, posterior, anterior.
The elbow joint is formed by the following bones:
- humerus;
- elbow;
- ray.
The anterior portion of the ulna has a rounded shape, while the posterior portion has a pointed shape.
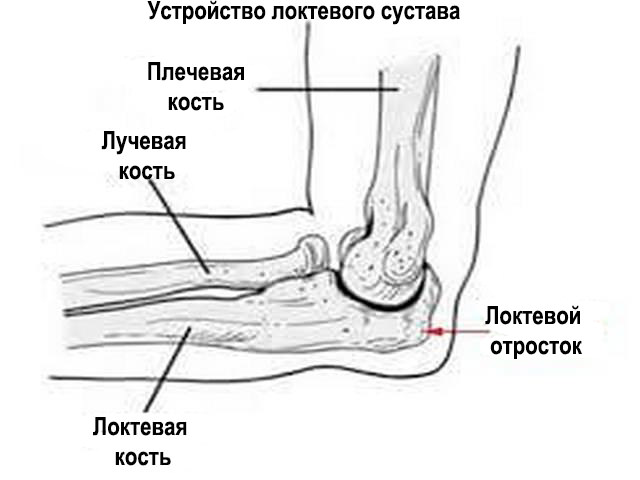
Rear area elbow joint directed towards the radius. In the anterior section is the head of the ulna.
The upper proximal epiphysis is thicker than the lower distal part. To avoid abrasion of the edges of the bone, which can occur due to the fact that a person constantly makes movements with his hands, the area of the trochlear notch is covered with articular cartilage. The coronoid and olecranon processes of the elbow joint are located along the edges of the trochlear notch.
Upper, lower areas The bones are connected to the radius by joints. External side The bone has a notch to accommodate the head of the radius. The coronoid process of the ulna is located above the anterior surface of the bone. The styloid process protrudes in the area above the wrist and can be easily felt.
Like all bones upper limbs In the human skeleton, the bony portion of the elbow is formed from the epiphyses and is connected to other bones.
The ulna, the anatomy of which has quite complex structure, requires careful handling. Therefore, it is recommended to be attentive to changes or discomfort. 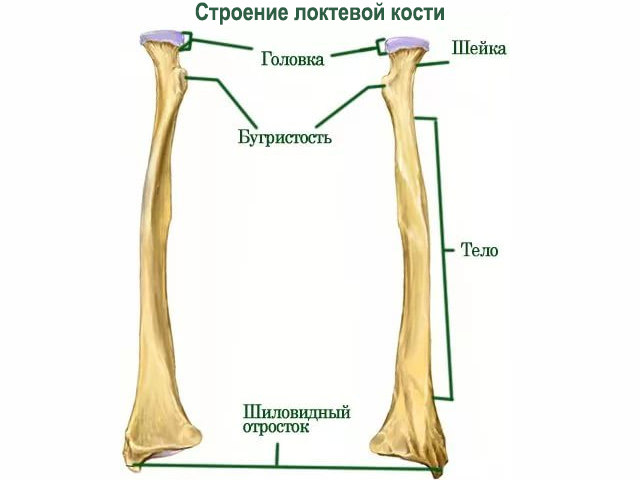
What function does it perform?
Due to the fact that this area has a complex structure, it allows you to perform the following movements:
- flexion;
- extension;
- supination;
- pronation.
For humans, these are necessary functions that help perform simple tasks. In addition, the human skeleton is complex mechanism, and the structure of the ulna is no exception. If one area of the elbow joint is damaged, the basic function of the arm as a whole will be impaired. Restoring elbow function is quite difficult, especially with serious injuries.
Possible diseases and damage
Often, injuries to the elbow area occur in children, athletes, and people over 60 years of age. In the case of children, this is due to constant movement and immature bones. Children's bones are fully formed around 10 years of age. Athletes get injured during falls or strong impacts.
For an elderly person to get injured, it is enough to fall on their hand, since over the age of 60 years, calcium is less absorbed in the body, and is washed out of it much faster. If there is not enough calcium, then damage will occur regardless of age category, gender or occupation.
There are several types of fractures that are distinguished in medical practice:
- Injury to the olecranon process. Basically, this damage occurs due to a fall or strong impact. The injury may be oblique or transverse in nature. In this case, the degree of bone displacement is taken into account;
- A dislocation of the bones of the forearm and a fracture of the olecranon process is called a Malgenya fracture: with the palm turned forward, the arm takes a semi-bent position. This damage requires the intervention of a neurosurgeon;
- A Monteggia fracture is considered to be a dislocation of the humeral head. There are open and closed form fracture In addition, from the side of the injury, the forearm visually appears shorter. The injury occurs in an extensor or flexion type, so its treatment directly depends on the characteristics of the injury;
- One of the most common injuries is an elbow fracture;
- Damage to the diaphysis in the form of a fracture of the central part tubular bone. IN in rare cases a displaced or comminuted fracture occurs. They are rare due to the fact that the radius bone is not damaged.
In addition to fractures, a bruise or dislocation, or less commonly, subluxation of a joint, can occur.
The development of diseases such as arthritis, arthrosis, and bursitis is considered a frequent occurrence. Each of them has its own characteristics in manifestation and therapy, but they should not be ignored. These pathologies extend specifically to the elbow joint.
The olecranon process of the bone is damaged in any area. In addition, this injury may be combined with other fractures in adjacent areas. The radioulnar and wrist areas are most often injured.
Symptoms of manifestation
There are a number of symptoms that will indicate the type of injury and its severity. Typically a fracture is characterized severe pain in the damaged area. Bruises and bruises often appear on the arm. Movement in to a large extent stiff due to pain. In some cases, bone deformation is observed.
If the fracture is open, then the bone can be seen through the wound. When open or closed fracture The patient has an enlarged limb due to edema.
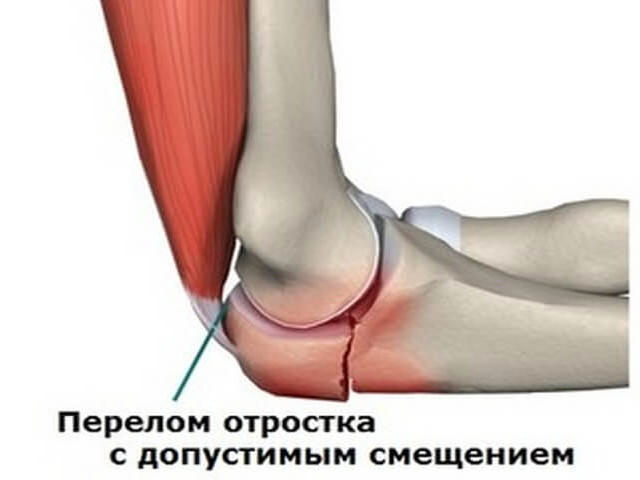
With a dislocation or subluxation, the victim feels pain where the injury supposedly occurred. Often the pain “spreads” throughout the entire limb. There is redness and swelling of the injured area.
A bone bruise is also painful. Bruises often occur during an impact with hard surface. The bruised area turns red, then swelling appears, after which the shade of the bruised area becomes blue or lilac.
First aid for injury
Depending on the type and degree of injury received, it is necessary to provide first aid to yourself or the victim. First of all, you will need to take a pain reliever if the pain has become unbearable. If there is a wound, wash it and carefully apply a bandage.
If you suspect a fracture, it is better to go to the hospital immediately. Until the doctors arrive, you need to immobilize your hand by applying a splint. It is important to be careful when doing this, as there is a risk of worsening the damage.
In case of injury, it is enough to apply cold compress on the injured area, and provide complete rest to the limbs. If there is a dislocation, you can also apply a compress, but in order to set the joint back, you will need the help of a specialist.
It is forbidden to try to set the bone yourself, regardless of the type of injury. Treating the wound with open fracture can only be done with disinfected hands. Any sudden movement will not only cause pain, but also increase the risk of complications. It is not recommended to apply a too tight and compressive bandage to the arm if a sprain occurs.
There is no point in delaying asking for help. If the fracture has open form, this threatens to infect the wound. Even if the fracture is closed, improper healing of the bone will cause severe discomfort to a person after healing, and this condition can only be corrected by re-fracture of the bone in a hospital setting. You should not let the situation get worse, as in some cases a fracture can lead to disability
Diagnostic methods
For appointment effective methods treatment is required correct diagnosis. During the examination, the doctor uses palpation to determine whether it is a fracture or another type of injury. An x-ray is then taken to view the location of the bone and determine the extent of the injury. After receiving the image, the doctor decides which treatment method is best suited.
Therapeutic measures
Treatment will depend on the type and extent of the injury. Usually, for fractures, a plaster bandage is applied if the bone has not been displaced or crushed. 7 days after applying the bandage, X-ray examination. This will ensure that complications such as displacement do not occur. Then you need to wear this bandage for at least 21 days, after which the plaster is removed.
In case of a displaced fracture, plaster will not help, so surgery is performed. Depending on the degree of damage, resection or installation of a plate with screws to secure the fragments is selected. To limb after surgical intervention was not exposed and did not move, a plaster splint is applied. This method takes significantly longer to heal. If necessary, the doctor will prescribe medications that will help reduce pain and speed up healing.
Installing metal plates is not for everyone. For example, not everyone old man will be able to endure the anesthesia that is necessary for installation. In addition, it is important to understand the severity of the fracture and limit yourself from sudden movements, negative impacts on a limb.
In case of bruises, it is enough to consult a doctor to get a prescription for ointment. Treatment of a dislocation requires the participation of a traumatologist. Often a dislocated bone needs to be realigned, otherwise the person's condition will worsen.
Important! It is important to remember that without consulting a doctor, self-medication will be dangerous to your health.
Rehabilitation measures
During rehabilitation, the main goal is to gradually prepare the damaged bone for future movement. It is important to do this carefully, not allowing a large volume of load at once or strong impact to the healing area.
To recover faster motor activity, physical therapy, massage, and physiotherapy are used. Physiotherapy consists of conducting UHF, magnetic laser therapy or electrophoresis, using paraffin or mud baths. These procedures are prescribed in accordance with the person’s condition.
In addition, it is recommended to make salt baths at home. They need warm water. The hand should be immersed in water for 15 minutes, preferably three times a day. This method is simple for a speedy recovery.
The massage is carried out with increasing intensity. Stroke from the hand to the elbow and back. Gradually you can begin to lightly rub and pat. This method should help the arm muscles not to lose tone; in addition, a properly performed massage helps to quickly restore the motor activity of the arm.
For some period of time after healing, it is not recommended to engage in active sports, since repeated injury can lead to serious health consequences.

After removing the plaster, after a certain period of time the doctor will prescribe physical therapy. It helps prepare the hand and reduce the risk of complications. Even 4 days after the plaster is applied, doctors recommend gradually starting to move your fingers. At first this may not work, but this activity is repeated several times daily, which allows you to gradually get used to it.
After 1.5 weeks, the muscles on the arm under the cast need to be tensed. After removing the cast, you need to rotate your forearm, carefully and without sudden movements.
Rolling a toy car on the floor will help develop your hand: just take a small children's toy car and roll it forward and then back along the floor surface. This exercise is designed to develop the flexion and extension process. A month after the cast is removed, you are allowed to lift dumbbells with light weight (no more than 2 kg).

Later, you are allowed to perform more complex exercises, which are individually selected by your doctor.
After a few months, it is allowed to play tennis or other games that require the elbow joint to work. It is advisable to avoid basketball, volleyball and similar games, as swipe on the arm will provoke re-injury.
Preventive measures
To avoid elbow fractures, it is recommended to take medications to maintain normal level calcium. You can increase your consumption of foods that contain it.
Don't give up on various active species sports, since the body, thanks to such activities, is greatly strengthened, however, do not forget about safety precautions when lifting weights or during sports activities, which require sudden hand movements. It is better to protect yourself with elbow pads or specialized anatomical bandages for the entire forearm. This will protect the bone from possible damage or at least reduce the risk of injury.

The structure of the human skeleton is one of the most complex. Each bone has its own special meaning and requires careful handling. By following safety and prevention rules, injuries can be avoided. You should not self-medicate, much less test the strength of your bones, since despite their strength, they are quite fragile.
Delaying a visit to the doctor if there is discomfort in this area is dangerous, especially if you were injured the day before. No one can be immune from fractures, and this damage, if not properly cared for, can lead to serious consequences.
Modern diagnostic and treatment methods allow for a quick recovery, however serious injuries require special care after healing has occurred. The risk of complications is quite high. The modern rhythm of life is not conducive to constantly strengthening your body, but observing preventive measures, it is possible to significantly reduce the risk of injury.
The ulna is a paired bone of the forearm. It consists of a bone body and two epiphyses - proximal and distal. The body of the bone is triangular in shape and has three edges - palmar (anterior), dorsal (posterior) and external (interosseous), as well as three surfaces. Fractures of the ulna are relatively rare and in most cases their treatment does not cause major problems.
Structure
The anterior edge of this bone has a rounded shape. And its rear edge is directed backwards. The interosseous edge has a pointed shape and faces the radius. The ulnar nutrient foramen leads into a proximally directed nutrient canal.
The proximal epiphysis has a slightly thickened shape and passes superiorly into the olecranon process. In front, the process is replaced by a trochlear notch, and it is limited by the coronoid process. Using the ulnar notch, located on the outer part of the coronoid process, this bone is connected to the articular circumference of the radius.
The shape of the distal epiphysis is slightly rounded, and the head of the ulna can be clearly seen on it. Its surface is smooth and concave, facing the wrist. Along its periphery is the articular surface - the circumference of the bone, which connects to the radius.
Fracture
Such a fracture is traumatic injury bones. It occurs quite rarely; fractures of the forearm bones are much more common. Isolated fractures of this bone occur in people of any age and gender. The cause of this fracture is a direct blow to the forearm. But Monteggia lesions usually occur in young men. They are formed when falling on the hand or when performing a defensive movement to deflect a blow with a bent arm.
Isolated fractures usually resolve without displacement of the ulna, and their treatment is not a problem. If such a fracture is combined with other injuries, then its course will be more severe, displacement and damage to the nerves are possible. In some situations, even surgical treatment is required.
Isolated fracture
More often this fracture happens transverse, fragments in such a situation are well held and displacement of the ulna is extremely rare. Displacement along the axis and length is also rare, since the entire radius bone helps to hold the fragments in place. Sometimes only angular displacement occurs, which must be eliminated.
For non-displaced fractures, a cast is usually applied for 6-10 weeks. If there are displacements, then reposition is performed and a cast is applied for 10-12 weeks. In rare situations it is necessary to carry out surgery, osteosynthesis of the ulnar diaphysis can be performed with a pin or plate. In such cases, after a fracture, exercise therapy and massage are recommended, as well as taking analgesics and antibiotics and UHF.
Monteggia damage
Monteggia injury is a high-energy injury and is more common in athletes. With such a fracture, there is a displacement of the ulna, as well as shortening of the forearm with dislocation of the head of the radius. At this damage deformation of the elbow joint and forearm is noticeable, as well as their swelling, bruising is possible. All movements are difficult; it is often possible to palpate the displacement of the ray head and find the places of displacement of bone fragments. There are also concomitant neurological and vascular disorders. Treatment of such injuries requires a stay in a trauma department and can be complex and lengthy. Sometimes, after this type of ulna fracture, it is not possible to fully restore the function of the arm.









